A payment gateway is a crucial technology that enables businesses and consumers to process payments seamlessly, both online and in-person. It acts as a secure bridge, allowing users to enter their payment details while safely transmitting the information to the relevant financial institutions for verification and approval. As global retail eCommerce continues to expand, projections indicate that it will grow from US $5.2 trillion in 2021 to US $8.1 trillion by 20256 reflecting the rapid digital transformation of the retail sector.
While these technological advancements provide businesses with opportunities to reach new markets and scale efficiently, they also create avenues for cybercriminals to exploit. According to Juniper Research, online payment fraud is projected to cost retailers over US $362 billion globally between 2026 and 2028. This highlights the critical need for secure payment solutions for retail that not only facilitate smooth transactions but also protect businesses and customers from evolving financial threats.
A safe and easy payment gateway is essential for securing consumer data and preventing payment fraud as more companies consider moving their operations online. This post will go over the advantages of payment gateways, how they operate, and how to pick the best option for your company. If your company doesn’t currently have a payment gateway, read on to see why it needs one.
What are the payment gateways?
A payment gateway is a piece of technology that allows businesses to take payments from consumers using credit or debit cards. The phrase refers to both the payment processing gateways available in online retailers as well as the actual card-reading equipment present in physical retail establishments. Additionally, physical payment gateways have started to take payments over the phone through Near Field Communication (NFC) or QR codes.
Important Takeaways
- Interfaces used to gather customer payment data are known as payment gateways.
- Point-of-sale (POS) terminals that take credit card information via a card or smartphone make up payment gateways in physical establishments.
- Payment gateways are the “checkout” portals in online retailers where customers enter their credit card details or login credentials.
- Payment processors, which use consumer data to collect payments on behalf of the merchant, are different from payment gateways.
- To make it easier to pay using cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, there are additional payment gateways.
What is payment gateway with example?
A payment gateway is a technological tool that enables companies to accept credit or debit card payments from customers. The term describes both the real card-reading devices seen in physical retail locations as well as the payment processing gateways offered by internet merchants. Furthermore, physical payment gateways have begun to accept phone payments via QR codes or Near Field Communication (NFC).
Examples
Stripe: It provides a friendly platform. It covers all businesses due to the advanced characteristics such as subscription management, fraud prevention, and also support multiple currencies.
PayPal: It is easy to use and it also has multiple options like credit/ debit card, Paypal balances, and other methods such as Venmo.
Square: is a well-liked option for small and medium-sized enterprises since it provides reliable point-of-sale (POS) solutions in addition to online payment processing.
Authorize.Net: an established participant in the payments market that offers retailers a safe and simple-to-integrate gateway.
Helcim: It is best for those companies who seek affordable and accurate costings.It is suitable for small to medium businesses .
How does the payment gateway works?
Payment gateways act as a middleman between your store and your customers, as was previously mentioned.
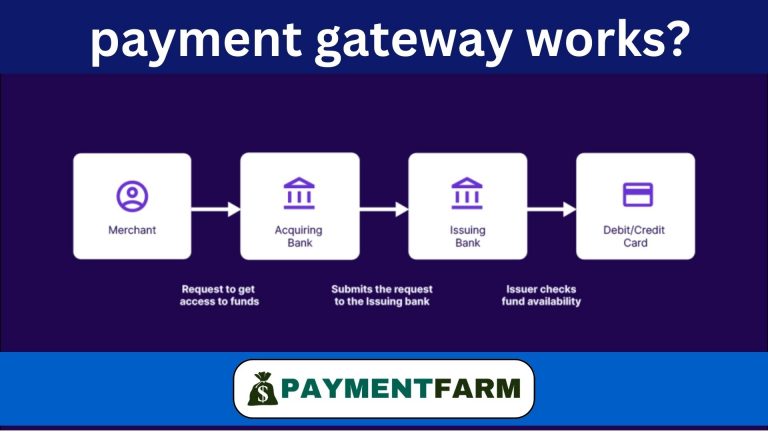
To carry out this process, the gateway connects with major debit and credit card networks, including American Express, Mastercard, Visa, and Discover, and communicates with the card issuer—the bank or financial institution that issued the card to your customer. Once connected, the gateway validates the legitimacy of the customer’s card details and transaction information.
After receiving confirmation from the issuer regarding the availability of funds and the accuracy of the transaction data, the gateway immediately notifies both the merchant and the customer whether the payment has been approved or declined. This real-time verification allows retailers to efficiently manage transactions, reduce payment errors, and enhance the overall payment solutions for retail experience.
Here's a more thorough explanation of how payment gateways operate:
- Either by using their credit card at a physical store or by inputting their information on the merchant’s eCommerce website, the customer starts a transaction.
- The acquiring bank, or the organization that handles payments on behalf of the merchant, receives the customer’s credit card information from the payment gateway.
- After establishing an interface with the customer’s card network (such as Visa or Mastercard), the payment processor forwards the transaction to the issuing bank, which is the bank that provided the customer with their credit card.
- The issuing bank confirms that the customer’s account has enough money in it to meet the purchase price. Determining if the transaction is fraudulent or not is another purpose for this phase. The bank will then decide whether to accept or reject the transaction.
What is a payment gateway service provider?
A business or platform that enables the safe processing of online payments between consumers and retailers is known as a payment gateway service provider. It serves as a middleman, securely transferring sensitive payment data, like credit card numbers, to banks, processors, or acquiring financial institutions via encryption.
Examples of Payment Gateway Service Providers:
- Stripe
- PayPal
- Authorize.Net
- Square
- Adyen
What is a payment gateway processor?
Two distinct systems that cooperate to enable electronic transactions are a payment gateway and a payment processor:
Gateway for payments: A mechanism that allows a business, a payment processor, and a customer to securely exchange payment information. Customer card information must be gathered and encrypted by payment gateways.
Processor of payments: The company manages the technical parts of processing payments, such as authorizing and settling money between the business’s bank and the customer’s bank. Other services including chargeback management, fraud detection, and payment regulation compliance may also be provided by payment processors.
What is a payment gateway fee?
The provider you select has a significant impact on the payment gateway fee. Nevertheless, the fee payment methodology is typically consistent across payment gateway providers.
For example, payment gateway service providers often charge a fee for each transaction that the solution processes. This frequently consists of a set cost on top of a percentage of the total transaction amount. Additionally, some providers are able to add their own prices. A number of other factors may also affect transaction fees. For example, the cost might remain at the typical rates listed above if you are processing a Visa or Mastercard payment card. However, the fees could pile up to a larger sum if you take American Express card payments. Payment card tiers also have a role to play. Certain credit cards are “qualified” and have their payments processed at a reduced cost if they comply with the processor’s guidelines. On the other hand, transactions made with other cards are charged more because they are considered “non-qualified.”
A payment gateway solution may also be subject to additional fees, such as monthly membership fees. This specific charge is typically rather small and might vary greatly. Having said that, these figures are subject to alter based on the provider you ultimately choose. Even though this is typically a minor fee, it’s crucial to evaluate it against those of other providers to ensure that you are not paying more than your fair share.
A payment gateway account may also be subject to a number of extra costs. In order to handle payments at their regular transaction rate, certain services have a minimum monthly threshold. You could have to pay more out of pocket if this threshold is not reached. This paradigm is maintained by several payment gateway businesses in order to safeguard their anticipated profits. With this monthly minimum cost, these payment gateway solutions typically recoup their losses if the volume of transactions falls short of your expectations.
Depending on the provider and the sector in which your company operates, there may be additional costs associated with payment gateway solutions. Even while most of the extra fees don’t cost much on their own, when you put them all up, they can grow out of control. Because of this, you should be aware of these fees, inquire about any additional costs that your possible payment gateway provider might impose, and compare the prices offered by other suppliers.
Before you join up for such a service, it’s crucial that you do your research and find out about all the associated expenses, as the total cost for your payment gateway account will differ depending on the provider. With our subscription-based business strategy, Stax provides clear pricing with no hidden costs and a 0% markup on direct-cost interchange, saving you up to 40% on processing fees.
What is payment gateway in e-commerce?
E-commerce payment processing is the technology that allows online shops to accept and manage electronic payments for goods and services. It entails the safe exchange of transaction information between clients, retailers, and payment service providers. The processor is responsible for authorizing, capturing, and settling money.
How does shopify payment gateway work?
Configuration and Integration: Shopify Payments can be enabled from the admin dashboard when you build a Shopify store. Since it is completely integrated into Shopify, there is no need for third-party accounts or services like PayPal or Stripe.
Client Checkout: After choosing a purchase and checking out, a customer is shown a number of payment choices that Shopify Payments supports, including local payment methods and credit/debit cards.
Processing Transactions: The payment processor receives the customer’s payment information securely encrypted by Shopify Payments. To confirm funds and authorize the transaction, the processor gets in touch with the client’s bank.
Distributions: Following a predetermined payout time (often 2–7 business days, depending on location), the money is transferred into the bank account you have linked once the transaction has been approved. Shopify Payments streamlines bookkeeping by combining all sales into a single payout.
Monitoring Payments: From the Shopify dashboard, you can monitor all payment statuses, including pending, paid, and refunded.
How does mastercard payment gateway work ?
Businesses may conduct in-person and online purchases with ease thanks to the scalable and secure Mastercard Payment Gateway. It ensures safe and efficient payment processing by serving as a mediator between the buyer, the seller, and the financial institutions. Here’s a summary of how it operates:
The client starts the payment process: When checking out, the customer chooses Mastercard as their payment option. They either authenticate using stored card data or enter their card information (number, expiration date, and CVV).
Encryption of Data: To guarantee security during transmission, the gateway encrypts the client’s private data. Unauthorized parties cannot access the data thanks to encryption.
Request for Transaction: The acquiring bank (the merchant’s bank) or payment processor receives the encrypted transaction details from the gateway.
Mastercard Network routing: The request is sent to the issuing bank (the bank that issued the customer’s card) by the acquiring bank via the Mastercard network.
Verification of Authorization: The bank checks that are being issued: The card’s validity (e.g., active, not expired). adequate money or credit limit. Fraud checks (e.g., comparing consumer behavior with transaction details).
Reaction: The acquiring bank and the payment gateway receive an approve or deny notification from the originating bank over the Mastercard network.
Confirmation of Payment: The payment gateway alerts the merchant if the transaction is accepted, enabling it to proceed. A purchase confirmation is sent to the customer.
Clearing and Settlement: Through the acquiring bank, the money is transferred from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account. Mastercard guarantees that every transaction is cleared and completed in accordance with global norms.
How does stripe payment gateway work?
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the Stripe Payment Gateway, a complete payment processing platform, makes it easier to accept payments both in-person and online:
The client starts the payment process: On a website or app, a consumer chooses a good or service and checks out. Among the many payment options that Stripe accepts are credit and debit cards (Visa, Mastercard, etc.). digital wallets, such as Google Pay, Apple Pay, and others. ACH, bank transfers, and more regional payment methods.
Integration with Stripe: Payment information is securely gathered by the merchant’s website or app using Stripe’s APIs or pre-built solutions (such as Stripe Checkout). Payment details (such as card number and CVV) are either handled through the merchant’s interface using Stripe Elements or directly entered into forms hosted by Stripe.
Encryption of Data: Stripe uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt sensitive payment information. To improve security, Stripe also employs tokenization, substituting a token for private card information.
Request for Authorization: The acquiring bank, which is the merchant’s bank, or a payment processor receives the encrypted payment information from Stripe. The customer’s issuing bank the bank that issued the card receives the request from the acquiring bank.
Identifying Fraud: Stripe uses Stripe Radar, an AI-powered tool that assesses transaction risks by analyzing data patterns, to carry out fraud checks. Rules can be altered by merchants to highlight or prohibit questionable activity.
Authorization by the Bank: The issuing bank confirms the validity of the card. availability of credit or money. adherence to security protocols, such as two-factor authentication using 3D Secure. Either approval or rejection is the issuing bank’s response.
Verification of Payment: If approved, Stripe tells the merchant’s system in real-time. The customer obtains a confirmation of the successful payment.
Restitution and Settlement: After combining all of the authorized transactions, Stripe deposits the money into the merchant’s bank account. Usually, payouts are made on a rolling basis (daily, weekly, etc.), less Stripe’s processing costs.
How does crypto payment gateway work?
A crypto payment gateway, also known as a crypto payment processor, is a service that allows merchants to accept cryptocurrency payments. It acts as an intermediary between the merchant and the customer, and the process works

The client starts the payment process: At checkout, the consumer chooses cryptocurrency as their payment option. They decide the particular cryptocurrency they wish to use for payment.
Creation of Invoices: A payment invoice, usually a unique wallet address (or QR code) for the transaction, is generated by the crypto payment gateway. If the product’s price is indicated in fiat (such as USD), the invoice indicates the amount to be paid in cryptocurrency, taking into account the current exchange rates.
The Client Provides Crypto: The client copies the wallet address into their cryptocurrency wallet or scans the QR code. They give their approval for the cryptocurrency to be sent to the specified wallet.
Verification of Blockchain: The applicable blockchain network such as Ethereum or Bitcoin is informed of the transaction. The transaction is verified by miners or validators, who also record it on the blockchain to ensure its legitimacy. Depending on the coin and network congestion, the confirmation process could take anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes.
Confirmation of Payment: The payment gateway instantly alerts the merchant when the transaction has been validated. The merchant can now process the order since it has been recognized as paid.
Fiat Conversion Option: To lower the danger of volatility, a lot of cryptocurrency payment gateways provide immediate conversion from cryptocurrencies to fiat money. For instance: The client uses Bitcoin to make the payment. The gateway deposits the corresponding amount into the merchant’s bank account after converting the Bitcoin into USD or another desired currency.
Restitution: The money stays in the designated cryptocurrency wallet if the merchant choose to keep the cryptocurrency payments. Within a predetermined time frame, the merchant’s bank or payment account receives the converted fiat currency.
To sum up
A payment gateway is a technological advancement that enables safe and easy online and in-store electronic transactions between consumers and retailers. It serves as a middleman, encrypting and sending private payment information like credit card numbers to processors, banks, or cryptocurrency networks for approval and settlement. With features like encryption and AI-powered risk assessment, payment gateways guarantee fraud prevention, expedite the checkout process, and accept a variety of payment methods (such as digital wallets, credit/debit cards, and cryptocurrencies). Well-known examples include PayPal, Stripe, and cryptocurrency payment gateways like BitPay, which provide companies with increased security for consumer transactions, flexibility, and a worldwide presence.
Faqs
What Is a Payment Gateway?
A payment gateway is a technology that enables businesses to securely accept electronic payments from customers, whether online or in-store. It acts as a bridge between the buyer, the merchant, and financial institutions, ensuring that payment information is transmitted safely and efficiently.
How Does a Payment Gateway Work?
When a customer initiates a payment, the gateway encrypts their payment information and sends it to the payment processor and issuing bank for verification and approval. Once the transaction is processed, the gateway instantly notifies both the merchant and the customer whether the payment has been approved or declined. This seamless operation ensures secure, real-time processing of transactions.
What Payment Methods Do Payment Gateways Accept?
Modern payment gateways for retail support a wide variety of payment options, including:
Debit and credit cards (American Express, Mastercard, Visa, Discover, etc.)
Digital wallets such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal
ACH payments and bank transfers
NFC payments and QR code transactions
Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, through specialized gateways
This versatility allows retailers to cater to a broad range of customer preferences.
Why Is a Payment Gateway Important for Businesses?
A payment gateway is essential for businesses because it:
Enhances Security: Encrypts sensitive payment data, lowering the risk of fraud and unauthorized access.
Improves Customer Experience: Ensures fast, reliable, and seamless payment processing, increasing customer satisfaction.
Supports Multiple Payment Methods: Allows businesses to reach a wider audience by accepting various types of payments.
Streamlines Operations: Automates transaction verification, reducing errors and administrative workload.
By implementing a robust payment gateway, retailers can provide secure, efficient, and flexible payment solutions for retail, which is crucial for maintaining trust and driving growth in today’s competitive market.
