In the fast-evolving world of business, few metrics matter more than the elusive “bottom line.” The bottom line represents a company’s net income, named for its position at the bottom of the income statement. By contrast, the “top line” refers to gross figures—specifically revenue—and often receives less attention despite its strategic importance. Top-line growth occurs when a company increases its revenue recognition, and it is a critical indicator of market demand, scalability, and long-term business potential.

For companies leveraging white-label payment solutions, accurately recognizing and reporting revenue in accordance with accounting best practices is especially important, as transparent financial reporting plays a key role in attracting investors and raising capital. obtain a loan, or boost their valuation. Accounting may not be the most attractive part of the business world, but it is unquestionably crucial to have a basic understanding of cash versus accrual. This information serves as the cornerstone for utilizing the revenue of recognition principles, which will ultimately increase your top line. However, what is exactly revenue of recognition? Continue reading to find out more about the basic principles of this system, how it is governed by US regulations, and how you may use it to meet performance goals and draw in investors.
What is revenue of recognition?
The process of documenting and reporting revenue inflows in a business’s financial accounts is known as revenue recognition. Based on the fulfillment of performance commitments, the transfer of control, and the amount that can be accurately quantified, it entails deciding when and how revenue recognition principles should be recognized. By ensuring that income is recognized accurately and on time, this accounting concept promotes openness and makes it possible for stakeholders to evaluate the financial performance of a business.
Revenue figures are the most important factor to consider when examining financial documents. To work with the right data for conducting business, your firm must ensure adequate and accurate revenue of recognition, measurement, and presentation. revenue recognition principles can be done in a number of ways, but not all of them work for every type of organization.
Revenue recognition 5 step model
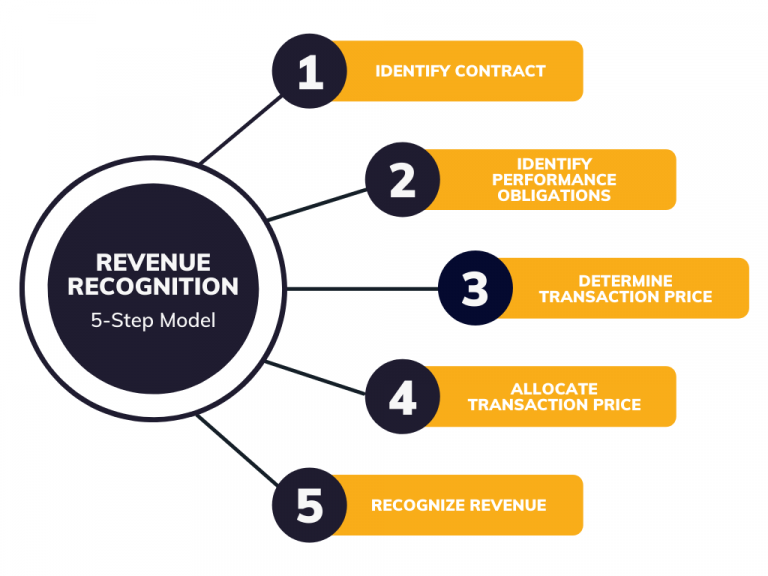
A set of procedures known as recognition of Revenue recognition criteria helps businesses accurately record and disclose their income in financial statements. These procedures guarantee prompt and correct revenue
- Determine the customer’s contract: Specify requirements for entering into a contract with a client.
- Determine the contract’s performance obligations: Establish clear responsibilities in the contract.
- Find the price of the transaction: When determining the cost of goods or services, take certain criteria into account.
- Decide on the purchase price: Rules for allocating the cost among various commitments.
- Revenue is recognized as soon as the organization fulfills a performance obligation: Describe how revenue is recognized when commitments are met.
In today’s increasingly complex business landscape, the traditional single-revenue model is quickly becoming obsolete. Modern companies must offer flexible, customized approaches to pricing, billing, and monetization to remain competitive. As accounting rules and standards continue to evolve, an already challenging revenue recognition process has grown even more complex. By leveraging a unified revenue recognition system, organizations can consolidate multiple income streams while ensuring compliance with the latest IFRS 15 and ASC 606 requirements. Such a system provides a comprehensive view of both recognized and deferred revenue, automates calculations, accelerates period-end close, and promotes transparency—empowering stakeholders to accurately assess the company’s financial performance.
Revenue recognition methods
Sales-based approach: When title passes to the buyer at the time of sale, revenue is recognized using the sales-basis method. This approach is frequently applied to transactions involving the sale of commodities, where revenue is recorded as soon as the buyer becomes the legitimate owner of the item. Because it synchronizes revenue recognition with ownership transfer, it offers a simple method for revenue recognition.
The completed-contract approach: At the conclusion of the contract, revenues and expenses are recorded using the completed-contract technique. For long-term projects when it is challenging to accurately predict the percentage of completion, this approach is usually employed. This method offers a more conservative approach to revenue recognition by only recognizing revenue and expenses upon contract completion.
Method of cost-recoverability: Profit recognition is postponed by the cost-recoverability technique until all project expenses have been reimbursed. This approach is frequently applied to projects where the recoverability of expenses is unknown. In order to prevent profit recognition until the project is judged financially feasible, revenue is only reported if all project expenditures have been recouped.
The method of percentage-of-completion: The percentage-of-completion technique, which is especially popular in long-term contracts, records income and expenses as a percentage of work accomplished. Using this approach, revenue and expenses are recorded in proportion to the percentage of work done as the project moves forward. This approach gives a more realistic picture of the project’s long-term financial success.
Method of installation: The installment approach is appropriate for transactions with erratic client collections since it records a proportionate profit upon installment receipt. Profit is recorded in proportion to the quantity of money received, and revenue is recorded as soon as the consumer makes a payment. When the collectability of payments is questionable, this approach enables more cautious revenue recognition.
Brokerage contract: A brokerage agreement complies with IRS and SEC regulations and proprietary rules for brokers. This approach specifies particular guidelines that brokers must adhere to while recording brokerage service revenue. It offers a uniform method of revenue recognition in the brokerage sector and guarantees adherence to tax and regulatory regulations.
The accrual method: Prepayments are first recorded as assets using the accrual technique, which then reclassifies them as expenses after the delivery and acceptance of goods or services. This approach more accurately depicts a company’s financial performance by matching revenue with the costs incurred to produce that revenue. Regardless of when money is received, it records revenue as soon as it is earned.
Method of appreciation: Real estate brokers can lower profits from selling properties at higher valuations by using the appreciation strategy. Revenue is recognized using this method in accordance with the property’s increasing value over time. It makes it possible to record income as the value of the property increases, giving a more realistic picture of the financial gain from the sale.
Method of proportional performance: The percentage-of-completion method for profit recognition is modified by the proportional performance method. Like the percentage-of-completion technique, it records revenue and expenses according to the percentage of performance that has been completed. This approach, however, bases profit recognition on the percentage of performance that is finished rather than the percentage of expenses incurred.
Method of deposit: Deposits covered by cancellation agreements are made using the deposit method. Although the deposit is recorded as a liability until the cancellation period has passed or the customer has met their commitments, revenue is recognized at the time of receipt through a modern payment gateway. By using this technique, revenue is kept from being recorded until it is absolutely assured that the deposit will not be refunded.
Deals Regarding Bill & Hold: The purpose of the bill and hold method is to stop fraudulent transactions that try to inflate a company’s assets. Even if the products are not delivered in person, revenue is recorded at the time of billing the consumer under this technique. Nonetheless, some requirements must be fulfilled, including the buyer’s request for the bill and hold arrangement, the products’ distinct identification, and their readiness for physical transfer.These different approaches give companies the freedom to recognize revenue according to the particulars of their transactions, guaranteeing accurate and trustworthy financial reporting.
Revenue recognition standard
ASC 606: The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) established ASC 606, which regulates nonprofit organizations and both public and private businesses in the US.
IFRS 15: The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) established the global standard known as IFRS 15. 167 nations, or nearly all developed nations outside of the United States, have adopted IFRS standards.
Both standards aim to reduce complexity while promoting standardization and comparability. The criteria differ in a few ways, including non-cash considerations, specific contract costs, and sales that are not part of regular business operations.
Everything you need to understand the revenue recognition principles
Revenue recognition is a core component of accrual accounting and defines the timing and method by which companies recognize, or record, revenue. Under this principle, revenue is recorded when it is earned rather than when cash is received, as is the case in cash accounting. This standardized approach promotes consistency, transparency, and accuracy in financial reporting, enabling organizations to reliably evaluate performance and communicate results to shareholders, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies. Regulatory authorities closely monitor how companies maintain their financial records to ensure revenues and expenses are reported uniformly and in accordance with established standards.
In the United States, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) mandates revenue recognition through Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). In 2014, the FASB collaborated with the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)—the organization responsible for accounting standards in more than 140 countries—to establish a unified global framework for revenue recognition. With the exception of the United States, India, and China, most major financial markets follow the IASB’s International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). While India does not fully adopt IFRS, it applies a closely aligned domestic standard.
Historically, global accounting regulations were largely industry-specific, leading to fragmented and inconsistent revenue recognition practices that made cross-industry comparisons difficult. To address this challenge, the FASB and IASB jointly introduced ASC 606 in the United States and IFRS 15 internationally. These standards provide a consistent, principles-based framework for recognizing revenue across industries and business models. They apply to public, private, and nonprofit organizations that enter into contracts to deliver goods or services. Even nonprofit and charitable entities benefit from accrual accounting, particularly when accounting for grants, government contracts, or recurring donations.
Revenue recognition policy

A component of accrual accounting known as revenue of recognition establishes the timing and method by which companies “recognize” or record their revenue. According to the idea, companies must record revenue in accrual accounting (when it is earned) as opposed to cash accounting (when payment is received).
Revenue recognition criteria
Performance commitments: A promise to deliver a unique good or service to a client is known as a performance obligation. The timing of revenue recognition depends on the identification of performance commitments.
Allocation of transaction prices: Every performance obligation in a contract should receive a portion of the transaction price. This entails giving each part or rendered service a value.
Collectability: One essential condition for revenue of recognition is collectability.
Reliability: It is important to consistently recognize and report new revenue.
Rewards and risks: The buyer should take on the risks and benefits of ownership instead of the seller.
Manage: The products sold should no longer be under the seller’s control.
Measurability: Both revenue and expenses should be quantified in a reasonable way.
What is revenue recognition principles in accounting?
To revenue recognition principles, there are five broad Revenue recognition criteria that must be satisfied. The requirements for revenue recognition are as follows:
- The contract has been approved by the parties, who also pledge to uphold its terms. Approval can be given verbally or in writing, depending on how it is typically given.
- It is possible to identify each party’s rights to the products or services that will be transferred.
- The terms of payment are obvious and unambiguous.
- The contract’s future influence on the risk, timing, or volume of future cash flows indicates that it has commercial substance.
- It is considered likely that “substantially all” of the money owed for the transfer of the products or services will be paid.
It is important to note that revenue cannot be recognized unless all of these requirements are satisfied.
To sum up
In conclusion, a fundamental idea in accrual accounting that controls how and when companies record their income is revenue of recognition. For proper financial reporting and transparency, it guarantees that income is reported at the time of earning
Rather than recognizing revenue when payment is received, standards such as ASC 606 and IFRS 15 provide a structured five-step framework to help businesses identify customer contracts, define performance obligations, determine transaction prices, allocate revenue appropriately, and recognize revenue when obligations are satisfied. Proper application of these guidelines allows organizations to present reliable and consistent financial information, enhancing comparability across industries, building stakeholder trust, and attracting investors by accurately reflecting underlying economic performance.
Faqs
Under IFRS, how is revenue recognized?
Recognizing revenue after the customer has received and is able to use the products or services is the fundamental tenet of IFRS 15. Accordingly, revenue cannot be recorded until the product has been delivered and accepted by the customer at the agreed upon price.
Which four factors go into revenue recognition?
The following are the four prerequisites for revenue recognition:
- A two-party agreement
- The completion of a service or the delivery of a product
- Obtaining payment from the client
- Understanding that the anticipated financial gain has been realized
What is the significance of revenue recognition?
Accurate and transparent financial reporting is ensured by revenue recognition. It assists stakeholders in evaluating a business’s financial performance, which is crucial for obtaining financing, drawing in investors, and adhering to legal requirements.
Usually, when is revenue recognized?
When a business completes its performance responsibilities under a contract and the client takes possession of the goods or services, revenue is often recorded.
